Most companies provide devices for their employees to perform their work for reasons such as security considerations, regulatory compliance, cost implications, and the balance between work and personal usage preferences within the company. A lot of times the employees misused the devices for their own usage or other purposes aside from their work. COPE (Company owned, personal enabled) policies create less monitoring towards the user’s usage of the company’s devices which increases the risk of data sabotage, data leaking, and misuse of devices that will damage companies’ properties and security compromise. As a SME, we’ve encountered the same issues as most companies where our employees deleted all the data in their company’s laptop and since then we’ve started BYOD policies to overcome it.

BYOD stands for “Bring Your Own Device.” It refers to a policy or practice where employees or individuals are allowed to use their personal electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, or laptops, for work purposes within an organisation.
BYOD has gained popularity in recent years due to the increasing prevalence of personal devices and the desire for flexibility and convenience in the workplace. Organisations may implement BYOD policies to reduce costs on hardware, increase employee satisfaction, and leverage the familiarity and productivity of employees with their own devices.
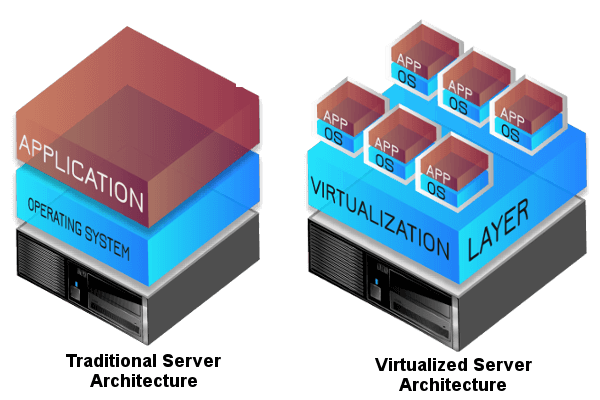
Thanks to virtualisation technologies, organisations can create secure, controlled, and efficient environments for employees to access company resources on their personal devices. These technologies help address security concerns, ensure data integrity, and provide a consistent user experience across various device types and platforms within a BYOD framework.
There are several reasons why you should start exercising BYOD,
- Cost Savings. Implementing BYOD can result in cost savings for the company. Instead of providing company-owned devices to employees, the organization can leverage employees’ personal devices, reducing the expenses associated with purchasing and maintaining hardware.
- Flexibility and Convenience. BYOD offers flexibility and convenience for employees. They can use their personal devices, which they already carry with them, for work-related tasks. This flexibility allows them to seamlessly transition between work and personal activities, potentially improving work-life balance.
- Technological Advancements. Personal devices often have the latest technologies and features, allowing companies to leverage these advancements without investing in regular hardware upgrades. This can provide access to cutting-edge capabilities and applications, enhancing efficiency and innovation.
- Rapid Adoption and Familiarity. BYOD policies leverage devices that employees are already familiar with, reducing the learning curve associated with new technologies. Employees can quickly adapt to using their own devices for work-related tasks, resulting in smoother integration and reduced training needs.
- Instant recovery in the case of hardware failure or theft. Employees access their workplace remotely, in the event that their personal hardware failed to operate, the company data still store securely in the cloud.
Believe it or not, there are many companies have started BYOD long ago but there are still many SME companies doesn’t know about this technology. It’s not the large enterprise that has the privilege to set up its own BYOD environment. Today’s virtualisation technologies have made the entire setup easier, more secure and lesser cost.
There are many desktop virtualisation software available in the market, these are the few popular ones,
- Microsoft Hyper-v. Hyper-V is a hypervisor-based virtualisation technology developed by Microsoft. It is a core component of the Windows operating system and allows for the creation and management of virtual machines (VMs) on Windows servers or Windows Desktops.

- Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops: Citrix offers a comprehensive desktop virtualization solution that allows organisations to deliver virtual desktops and applications to end-users. It provides centralized management, user access controls, and advanced features like application virtualisation.

- VMware: VMware is a desktop and application virtualization platform that provides secure access to virtual desktops and applications. It supports a variety of endpoints and offers features like unified management, instant cloning, and GPU virtualization.

- Parallels: Parallels provides virtual desktop and application delivery to end-users. It supports various hypervisors, offers load balancing and failover capabilities, and integrates with Microsoft RDS.

- Oracle Virtualbox: Oracle Virtualbox is a desktop virtualization solution that enables the deployment and management of virtual desktops. It supports multiple client devices and provides centralized administration and monitoring.

- Red Hat Virtualisation for Desktops: Red Hat Virtualization for Desktops is a desktop virtualization platform based on the KVM hypervisor. It enables organizations to create and manage virtual desktops and provides features like high availability, live migration, and centralized management.

While Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies offer several benefits, they also come with potential disadvantages and challenges. Here are some of the drawbacks associated with BYOD:
- Security Risks. Virtual desktops require remote access to access. It increases the risk to allow unauthorised users to access the remote desktop by just having the user password.
- Legal and Compliance Concerns. BYOD raises legal and compliance considerations. Data protection and privacy regulations may impose specific requirements on how company data is handled and secured on personal devices. Organizations need to navigate these regulations, implement proper policies, and ensure employee compliance to avoid legal and regulatory repercussions.
- Support and Maintenance. Supporting a wide range of personal devices can be a challenge for IT departments. They may face difficulties in providing comprehensive technical support, troubleshooting device-specific issues, and ensuring timely software updates and patches across various platforms.
- Server failure. In the event that the core server that empowered your entire organisation’s virtual desktop has failed, it could affect your entire operation which depends on one single server to operate.
- Cost Considerations: While BYOD can provide cost savings in terms of device procurement, it may incur additional costs for implementing security measures, device management tools, and technical support. Organizations need to carefully evaluate the overall cost-benefit analysis of BYOD to ensure it aligns with their financial objectives.
To mitigate these disadvantages and risks, organisations can implement strong security policies, access restrictions with VPN, regular backup with RAID technologies, host your server securely, educate employees on best practices, and establish clear guidelines and agreements for BYOD usage.
